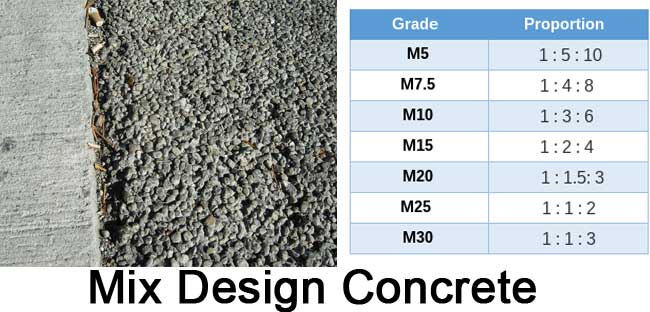
Mix Design Concrete Calculation – M20, M25, M30, M35
The process of selecting suitable ingredients of concrete and determining their relative amounts with the objective of producing a concrete of the required, strength, durability, and work ability as economically as possible, is termed the concrete mix design.
A concrete mix of inadequate workability may result in a high cost of labor to obtain a degree of compaction with available equipment.
From a technical point of view, the rich mixes may lead to high shrinkage and cracking in the structural concrete, and to the evolution of high heat of hydration in mass concrete which may cause cracking.
Requirements of Concrete Mix Design
The requirements which form the basis of selection and proportioning of mix ingredients are:
- The minimum compressive strength required from structural consideration
- The adequate workability is necessary for full compaction with the compacting equipment available.
- Maximum water-cement ratio and/or maximum cement content to give adequate durability for the particular site conditions.
- Maximum cement content to avoid shrinkage cracking due to the temperature cycle in mass concrete.
Types of Mixes
A. Nominal Mixes
In the past, the specifications for concrete prescribed the proportions of cement, fine, and coarse aggregates. These mixes of the fixed cement-aggregate ratio which ensures adequate strength are termed nominal mixes.
B. IS 456-2000 has designated concrete mixes into a number of grades as M10, M15, M20, M25, M30, M35, and M40. In this designation, the letter M refers to the mix and the number to the specified 28-day cube strength of mix in N/mm2.
C. Design Mixes
In these mixes, the performance of the concrete is specified by the designer but the mix proportions are determined by the producer of concrete, except that the minimum cement content can be laid down.
Factors Affecting the Design Mix
1. Compressive strength
It is one of the most important properties of concrete and influences many other describable properties of the hardened concrete. The mean compressive strength required at a specific age, usually 28 days, determines the nominal water-cement ratio of the mix.
2. Durability
The durability of concrete is its resistance to aggressive environmental conditions. High strength concrete is generally more durable than low strength concrete.
In the situations when the high strength is not necessary but the conditions of exposure are such that high durability is vital, the durability requirement will determine the water-cement ratio to be used.
3. Maximum nominal size of aggregate
In general, larger the maximum size of aggregate, smaller is the cement requirement for a particular water-cement ratio, because of the workability of concrete increases with an increase in the maximum size of the aggregate.
4. Grading and type of aggregate
The grading of aggregate influences the mix proportions for a specified work ability and water-cement ratio. Coarser the grading leaner will be mix which can be used.
A very lean mix is not desirable since it does not contain enough finer material to make the concrete cohesive.