Short Column Vs Long Column | Differences in Short and Long Column
The two types of columns utilised in the construction are long and short columns. The column is a vertical structural component that will be compressed vertically.
The compressed load’s line of action will travel via the axis of the columns, or it may run parallel to the axis of the columns.
What is Column?
Columns, struts, and pedestals are commonly employed as compression components in structures such as buildings, bridges, tank support systems, industries, and many more.
A column is a vertical compression member that is primarily subjected to axial loads larger than three times the least lateral dimension and effective length.
Pedestal is a compression member whose effective length is less than three times its shortest lateral dimension. Strut refers to a compression part that is inclined or horizontal that is subjected to axial loads. In trusses, struts are employed. The purpose of columns is to distribute the weight of a construction vertically downwards to a base.
- It divides the building into separate parts and gives privacy.
- It protects you against intruders and insects.
- It keeps the building warm in the summer and winter when the weather is cool.
What is Short Column?
Short columns are defined as those with a ratio of less than 12 between the efficient length of the columns and the lowest lateral dimension of the columns.
Short Column Important Characteristics:
- Only crushing or direct compression will cause small columns to fail.
- Rankine’s principle will apply in these types of columns.
- The lateral dimensions will be greater than the column length.
- There will be a slenderness ratio of less than 45.
- While the effective length of the columns to the lowest lateral dimension of the columns will be less than 12, the ratio of the effective length to the lowest lateral dimension of the columns will be less than 12.
- When the column length is lowered, the load-carrying capacity of short columns increases.
What is Long Column?
We must determine the group of columns during the design phase, which is separated into two groups based on the length and lateral dimensions of the columns. Long columns are those that have a ratio of the efficient size of the column to the least lateral dimension of the column that is larger than 12.
Long columns Important characteristics:
- Buckling or bending will cause long columns to fail.
- Euler’s theory will be used for longer columns.
- The lateral dimension will be considerably smaller than the column length.
- The slenderness ratio will be more than 45.
- While the effective length of the columns will be more than the lowest lateral dimension of the columns, the ratio of the effective length to the lowest lateral dimension of the columns will be less than 12.
- The load-carrying capacity decreases as column length increases.
Column Failure Mode
- One of three things can cause a column to fail
- Concrete or steel reinforcing compression failure
- Buckling
- Failure due to a combination of compression and buckling
- Short and stocky columns are more likely to fail due to compression failure
- Buckling is more likely with a long, narrow column
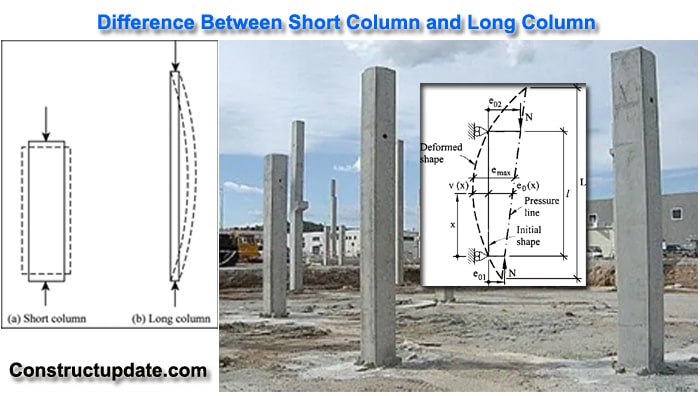
Difference between short column and long column
Short Column :
- If the ratio of effective length to the least lateral dimension of a column is less than or equal to 12, it is considered to be short.
- The ratio of a short column’s effective length to its smallest gyration radius is less than or equal to 40.
- The likelihood of buckling is extremely minimal.
- When compared to a long column with the same cross-sectional area, the weight carrying capacity is higher.
- Crushing is the cause of short column failure.
Long Column :
- If the ratio of a column’s effective length to its smallest lateral dimension is more than 12, the column is said to be long.
- The ratio of a long column’s effective length to its gyration radius is greater than 40.
- Long and slender columns are prone to buckling.
- A long column has a lower load-carrying capacity than a short column with the same cross-sectional area.
- When it comes to buckling, the column usually fails.